My previous deep dives into Google Cloud Agentspace, Agentspace UI Overview and Agentspace Connectors and Actions , established how its user experience and robust data integration (via Connectors and Actions) deliver significant value through enhanced enterprise search and summarisation.
While this provides a powerful foundation, the true promise of Agentspace lies in moving from insights to action. That’s where Agentspace agents come in.
This article will first introduce you to DeepResearch, Google Cloud’s initial pre-configured agent. We’ll then explore how you can use Agentspace’s no-code development tool to build your own custom AI agents, looking at the capabilities, features, and benefits this provides for automating tasks and boosting your operational efficiency.
Agentspace Agents
While the Enterprise Search and summarisation features in Agentspace deliver significant value to an organisation through enhanced workforce efficiency and productivity (and the associated cost savings), the platform unlocks its transformative potential with the introduction of agents. These are specialised AI assistants, powered by Google’s state-of-the-art Large Language Model: Gemini, engineered to move beyond simple information access towards proactive task execution and intelligent workflow automation. Agents excel at tackling complex, multi-step challenges, orchestrating actions, and integrating capabilities across various enterprise systems. They achieve this by combining information retrieval with advanced reasoning and the ability to execute defined actions, effectively automating entire processes, driving deeper efficiency gains and enabling new levels of operational capability.
Google’s DeepResearch Agent
Out of the box (OotB), Agentspace features Google’s DeepResearch agent, designed to perform comprehensive analysis on a given topic. Its ‘deep analysis’ involves synthesising information from diverse data sources (including configured enterprise data sources and the public web) to generate novel insights and structured understanding that go beyond simple keyword searches. For instance, instead of just getting a list of search results, imagine asking DeepResearch to investigate ‘customer reactions to our latest product update.’ DeepResearch could analyse feedback from your customer support system, comments on your community forum, and public social media posts. It would then deliver a synthesised report highlighting:
- The top 3 things customers love about the update.
- The 2 most common complaints (e.g., “the new interface is slower on older devices” or “feature X is harder to find now”).
- Perhaps even an unexpected insight, such as “many users are asking for a tutorial on a specific new function,” or “customers in the UK are responding more positively than those in the US.”
This kind of structured summary, with findings clearly identified and traced back to the original information sources, is far more actionable than raw search output.
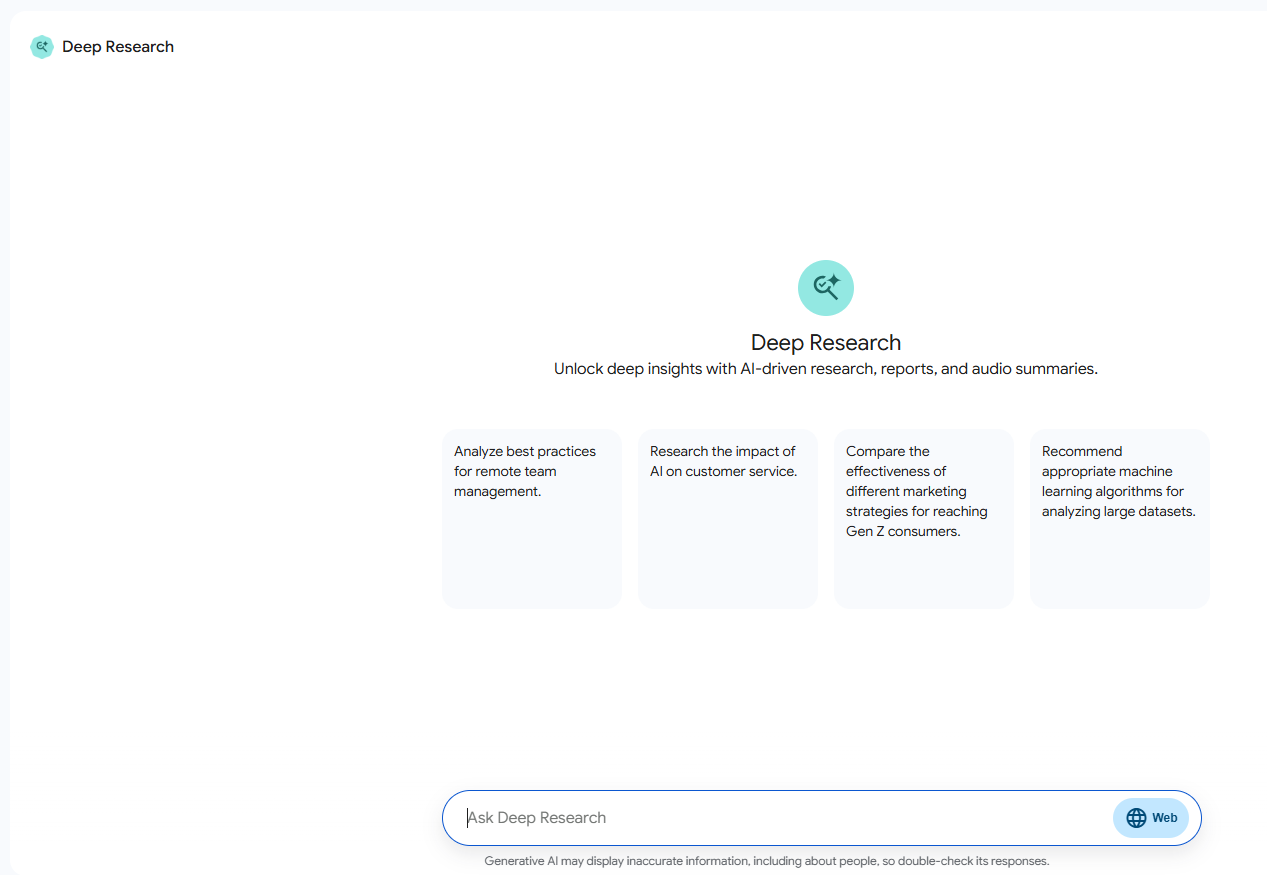 Figure 1: Screenshot of Google’s initial agent: DeepResearch
Figure 1: Screenshot of Google’s initial agent: DeepResearch
A defining characteristic of the DeepResearch agent is its emphasis on user control for complex tasks: it first presents a detailed research plan outlining its intended steps, potential sources, and expected lines of inquiry. The user reviews and approves this plan before the DeepResearch proceeds with the execution. This human-in-the-loop (HITL) mechanism ensures the research aligns with the user’s intent and allows for oversight before extensive processing occurs.
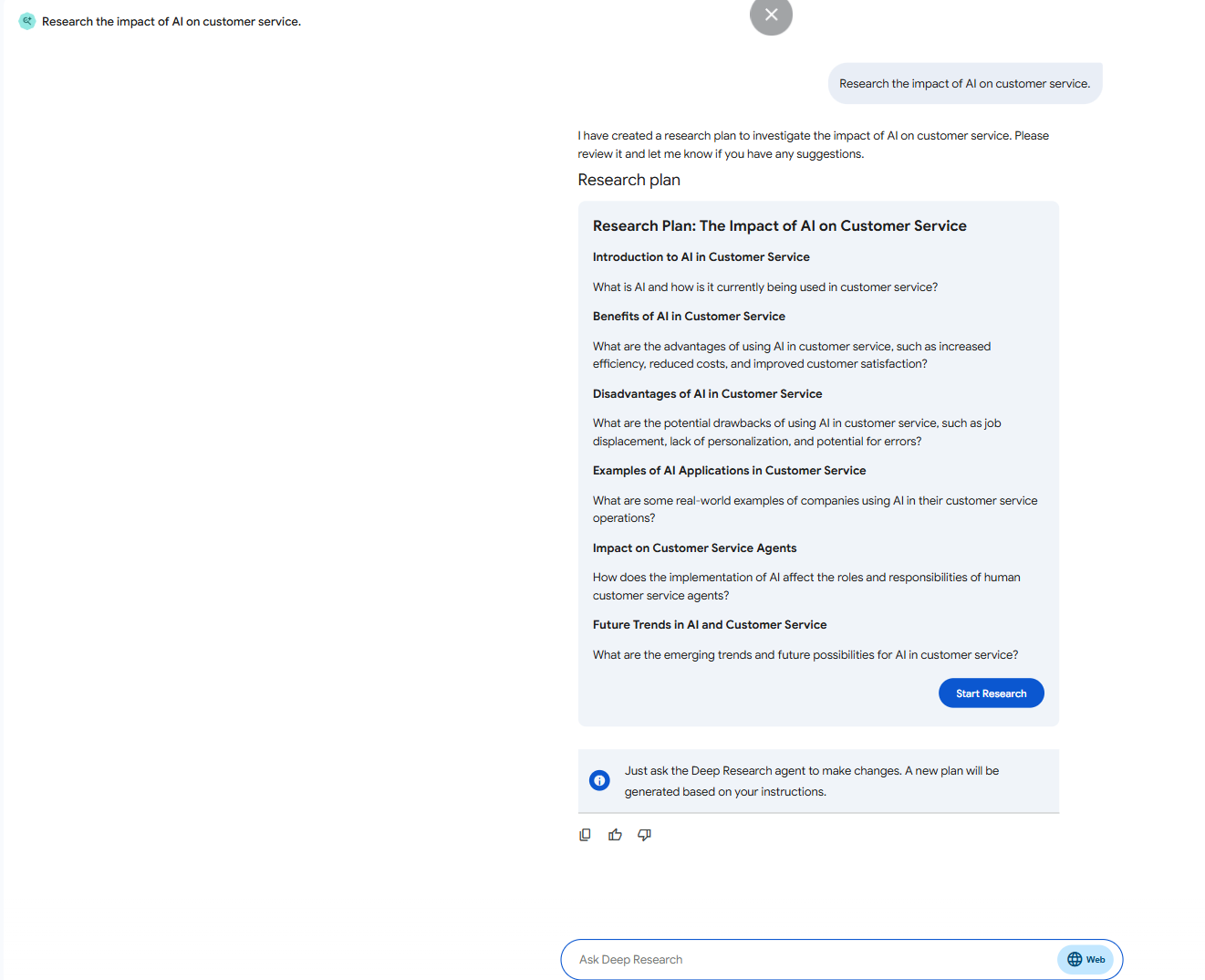 Figure 2: Screenshot of Google’s DeepResearch Agent Plan for Query: “Research the impact of AI on customer service.”
Figure 2: Screenshot of Google’s DeepResearch Agent Plan for Query: “Research the impact of AI on customer service.”
Upon approval, the DeepResearch agent executes the plan, returning a detailed, structured report of its findings along with citations and an audio summary.
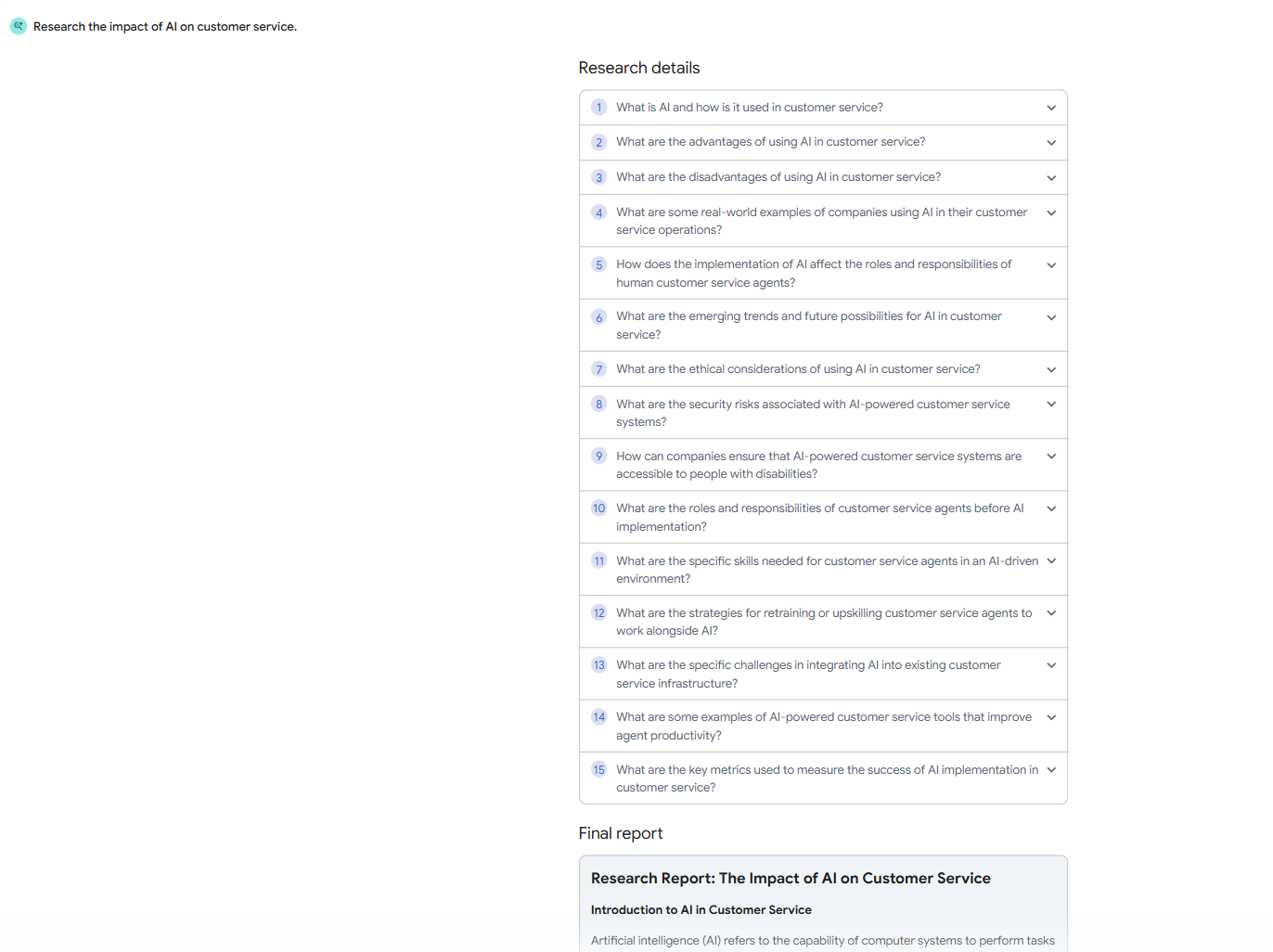 Figure 3: Screenshot of Google’s DeepResearch Agent Execution Steps for Query: “Research the impact of AI on customer service.”
Figure 3: Screenshot of Google’s DeepResearch Agent Execution Steps for Query: “Research the impact of AI on customer service.”
 Figure 4: Screenshot of Google’s DeepResearch Agent Report for Query: “Research the impact of AI on customer service.”
Figure 4: Screenshot of Google’s DeepResearch Agent Report for Query: “Research the impact of AI on customer service.”
Whilst DeepResearch is the debut Google provided agent OotB, the Agentspace UI is clearly structured to accommodate a growing ecosystem of agents. It features dedicated sections for preconfigured ‘Google Agents’, ‘From Your Organisation’ agents (custom agents shared within the company), and ‘Your Agents’ (personal custom agents). This design suggests Google’s intention to release additional preconfigured agents in the future…
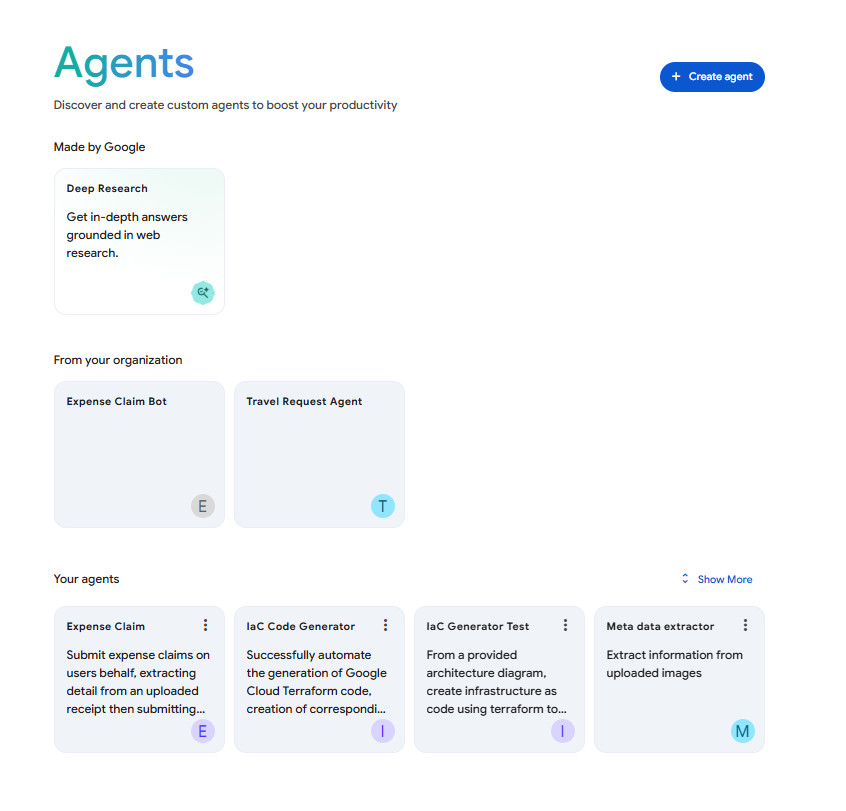
Figure 5: Screenshot of Agentspaces Agents UI.”
Custom Agents
Custom agents truly embody the principles of agentic AI, offering maximum value to enterprises by allowing the tailoring of AI capabilities to specific business needs and processes. It’s likely that many unique organisational workflows will require custom agents to effectively oversee their specific nuances. These agents are powerful because they are grounded in your enterprise data sources and leverage company specific tools and actions alongside their core reasoning abilities to achieve defined goals.
Agentspace provides a ‘no-code’ interface for creating these custom agents, empowering individuals who deeply understand business processes, yet may lack traditional programming backgrounds, to build their own.
Custom agents within Agentspace are created through a few simple steps, primarily using natural language prompts:
- Define a name for the agent: A clear, descriptive name helps identify its purpose.
- Define a goal for the agent: This concisely explains what the agent is designed to achieve.
- Define instructions for the agent: This is where you detail the agent’s scope, capabilities, objectives, and the methods it should use. You can specify response formatting, conditions for its actions, and the tools or actions it should call.
Crafting these instructions is key to creating an effective agent. It relies on principles like prompt engineering: instructions must be specific, unambiguous, and provide sufficient context. Defining the perfect instructions is an iterative process. Expect to test, observe the agent’s behaviour, and refine your prompts to achieve optimal performance. To assist with this, after drafting initial instructions, Agentspace includes a handy ‘help me write’ button. This feature leverages AI to analyse your input and suggest improvements for clarity, completeness, and efficiency, often incorporating best practices in prompt engineering to make your agent more effective. This AI-assisted instruction refinement is a form of meta-prompting, where Generative AI helps you craft even more descriptive and potent instructions from your initial ideas!
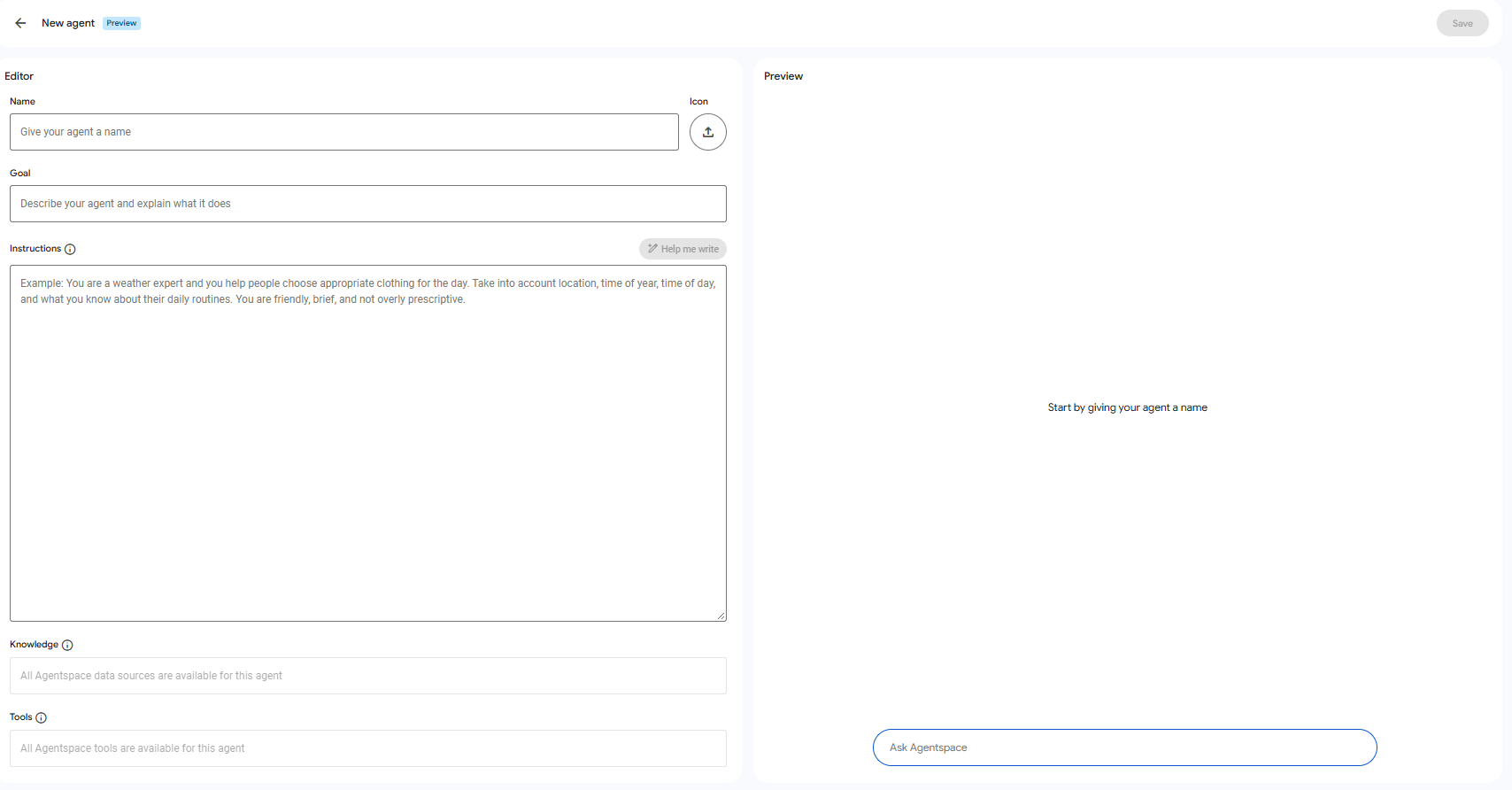
Figure 6: Screenshot of Agentspaces Custom Agent No Code UI.”
Agent Tools and Actions
Tools and actions within the Agents configuration specify the capabilities the agent can leverage to interact with the outside world or perform specific functions. This goes beyond just invoking predefined ‘Actions’ within Agentspace. You can grant the agent access to a variety of tools, such as calling external REST APIs (e.g., to update a customer record in your CRM or fetch real-time shipping information for an order), triggering Cloud Functions for custom backend logic, utilising specialised Vertex AI Tools like Vertex AI Search for advanced retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) across your documents, Vertex AI Vision for image analysis tasks (such as reading a product label from an uploaded photo), or the Natural Language API for sentiment analysis within a custom tool workflow. You can also enable interaction with databases via configured connectors, or the execution of other custom-built functions.
Under the hood, this relies on the underlying Large Language Model’s ability for tool use (often referred to as function calling). The LLM uses its advanced reasoning capabilities to understand the user’s intent and the agent’s overall goal. It then intelligently determines when to employ a specific tool from its available toolkit, and crucially, how to generate the correct parameters for that tool based on the ongoing conversational context and its ultimate objective.
At the time of writing (May 2025), Agentspace agents currently have access to all Tools. However the UI has a field that will enable filtering the available tools in a future release.
Agent Grounding
The agents can access relevant enterprise knowledge using the Connectors you’ve configured (as discussed in the previous post on Agentspace Connectors and Actions ). This step is crucial for grounding the agent, ensuring its responses, reasoning, and actions are based on factual, up-to-date company information rather than solely relying on the LLM’s general pretrained knowledge, thereby minimising hallucinations, improving accuracy, and building user trust in the agent’s outputs. This effectively leverages the principles of Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG), providing specific, timely context pulled from your data sources to inform the agent’s task execution.
At the time of writing (May 2025), Agentspace agents currently have access to all configured datasources (as per calling users permissions). However the UI has a field that will enable filtering the available tools in a future release.
Agent Invocation
Once created, interaction with custom agents occurs within the unified Agentspace UI, where they appear alongside other features, often under a dedicated menu section. Users engage with the agent using natural conversation through the chat interface to initiate tasks and receive assistance.
Benefits of No-Code Agents
The availability of a no-code agent design approach provides many benefits to an organisationincluding:
- Accessibility & Empowerment: It significantly lowers the barrier to entry, empowering non-technical users who are closest to the business challenges to directly design and implement AI solutions tailored to their specific needs. They no longer need to solely rely on development teams that can quickly become a bottleneck.
- Speed & Agility: Development cycles are dramatically accelerated. Building, testing, and iterating on custom agents can be done much more rapidly when visual tools replace complex coding, allowing organisations to respond quickly to changing business requirements.
- Focus on Business Logic: Users can concentrate on what they want the agent to achieve, and the business rules it should follow, rather than getting bogged down in the how of technical implementation. The interface abstracts away the underlying complexity.
- Reduced Development Costs: While not eliminating the need for technical oversight entirely, it can reduce the direct hours and reliance on specialised AI developers for many common agent creation tasks.
- Increased Innovation: By enabling a broader base of employees to experiment and build, organisations can foster a culture of innovation, uncovering new ways to automate processes and improve efficiency that might not have been identified by a central IT team alone.
This no-code interface shifts agent creation from a complex technical task to a more accessible business capability, allowing for faster delivery of custom AI solutions that directly meet enterprise requirements.
Agent Reasoning and Orchestration
Beyond simply executing individual commands based on their instructions and tools, a core strength of Agentspace agents lies in their reasoning and orchestration capabilities. When presented with a complex goal, agents don’t just perform a single action. Instead, powered by the LLM (Gemini), they intelligently break down the request into smaller, logical steps. Many agents employ methodologies conceptually similar to ReAct (Reason + Act), where they internally ‘think’ about the current state and goal, decide on the next best action (e.g., Thought: ‘The user wants to book a flight. First, I need to know their destination and dates. I should ask for that.’ Action: Ask user for destination and dates.), execute that action, observe the outcome (e.g., Observation: ‘User provided destination: London, Dates: July 10-15.’), and then repeat the reasoning process to determine the subsequent step (e.g., Thought: ‘Now I have the destination and dates, I need to check flight availability. I should use the Flight Search tool.’ Action: Call Flight Search tool with parameters London, July 10-15.).
This iterative cycle of reasoning, acting, and observing allows agents to dynamically navigate complex, multi-step workflows. The explicit ‘plan’ presented for approval by the DeepResearch agent is a visible example of this planning capability in action, providing transparency for intricate tasks. Custom agents utilise similar, though often internal and implicit, reasoning processes to orchestrate the sequence of operations needed to achieve their specific objectives. This means they might not always present an explicit plan for pre-approval like DeepResearch (unless specifically designed to incorporate such checkpoints for user validation), but the underlying LLM still performs this multi-step reasoning to sequence actions effectively. This could involve gathering information from multiple sources, making sequential decisions based on evolving data, or interacting with several different systems to complete a task like processing an expense claim (as detailed in the example below).
Agentspace Custom Agent Example Use Case
An example custom Agentspace agent we can conceptualise involves simplifying expense claim submissions. Depending upon the system and the user’s experience submitting expense claims, this can be a time-consuming and challenging process. For users that don’t frequently submit expenses, they often need to find documentation or a colleague to guide them through the process (something that could otherwise be done via Enterprise Search in Agentspace with a simple KB article). Once they have identified the system, they then need to authenticate and then navigate the UI, submitting and classifying the expense claim, whilst trying to ensure adherence to corporate expense policies.
With a custom agent, this process can be significantly simplified and managed from within the Agentspace UI.
- The user uploads an image of a receipt they want to claim expenses for to the ‘Expenses Agent.’
- The agent identifies the uploaded file as an image and processes it as a receipt, leveraging the built-in multi-modal capabilities of Agentspace/Gemini, for image understanding and initial data extraction from the receipt.
- It then extracts key information like the date, vendor, items, and cost. These details are used to classify the expense type, comparing item descriptions against a company’s predefined expense categories (or using the LLM’s reasoning for classification based on learned patterns).
- The agent also checks if the expense aligns with the defined company expense policy in real time.
- The agent then submits the extracted data alongside additional information it knows about the user (e.g., name, email address, department), which it retrieves from the user’s Agentspace profile (or by querying an internal employee directory via a connected tool).
- It prompts the user within the Agentspace chat interface to validate the detected information, add any missing mandatory data not stored in the user profile or on the receipt (e.g., cost centres, project codes), and confirm compliance with policy if any flags were raised.
- The agent then transfers the validated data into a structured format like JSON, prior to submitting the expense request to the corresponding backend system, for example, by using a custom tool that calls the company’s expense management system’s REST API.
- Finally, the agent emails confirmation of the expense claim submission to the user, providing a record of the transaction alongside links to documentation for expense FAQs.
This agent provides a better customer experience for the person submitting the expense claim, improves efficiency as the entire process is managed and guided by the agent who is available 24/7, ensures improved compliance with expense policies through proactive checks, and caters for validation and correct submission of expense claims, reducing the likelihood of user error due to inexperience.
Agentspace Where Next?
Agentspace already delivers substantial value with its current suite of features for Enterprise Search, Summarisation, and custom agent driven process automation. However, the field of agentic AI is evolving rapidly, and looking ahead, a couple of key developments could unlock even more potential within the platform:
-
Advancing Agent-to-Agent Collaboration: The recent buzz around Google’s Agent-to-Agent (A2A) communication protocol (announced at Google Cloud Next ‘25) points to an exciting future. Currently, building very complex workflows in Agentspace can sometimes lead to highly intricate instructions for a single agent managing multiple sub-tasks. Enhanced native A2A capabilities within Agentspace would allow for the development of more modular, specialised agents that can collaborate seamlessly. This aligns with agentic AI design principles, where smaller, focused agents are often easier to develop, manage, maintain, and scale.
-
Broadening Integration and Interoperability: The ability to easily integrate or import agents developed outside of the core Agentspace environment would be another significant leap forward. If agents built with Google’s Agent Development Kit (ADK), or agents running on Vertex AI Agent Engine (or other open source frameworks and platforms) could be seamlessly brought into Agentspace it would offer a powerful solution to orchestrating diverse, specialised agents (potentially addressing the first point as well), but would also dramatically expand the accessible toolkit for enterprises, unleashing further innovation.
While these areas represent exciting opportunities for growth, Google’s deep commitment to pioneering AI and agentic technologies paints a promising picture for the continued evolution of Agentspace. The journey towards intelligent, autonomous enterprise operations is accelerating, and platforms like Agentspace are pivotal in shaping that future. I’m looking forward to seeing how Agentspace develops throughout 2025!